CASE STUDY
EducationXR
Fully immersive, multi-user education & training platform for VR, desktop, tablet, & mobile devices
EducationXR
0 to 1 Journey
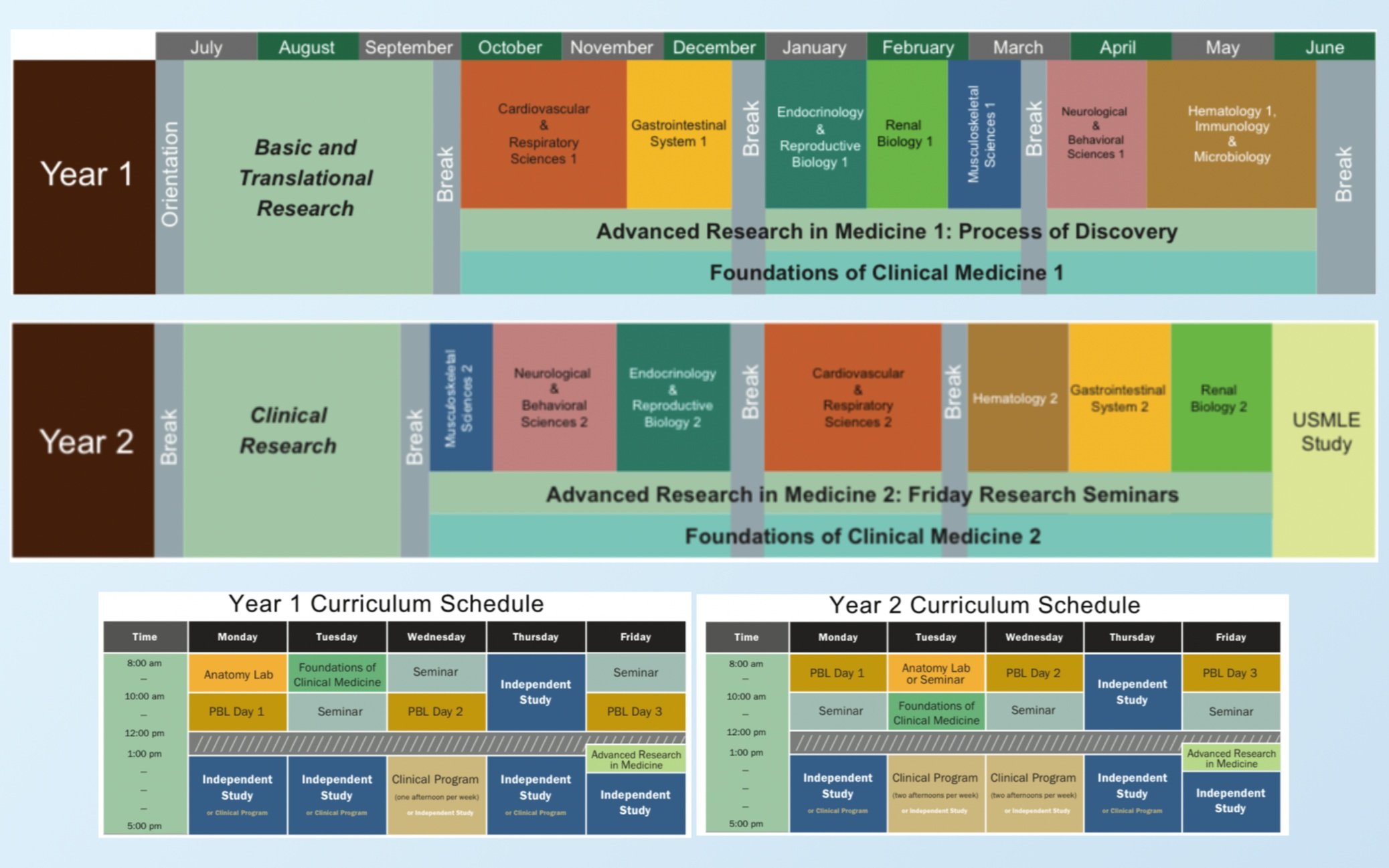
Launching a VR-based learning platform for 1st and 2nd year anatomy students at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine in less than 10 months.
CONTEXT
In December 2018, I was recruited by Heizenrader as VP of Product to lead a significant project: developing a VR-based education platform for the newly established Cleveland Clinic Learner College of Medicine at Case Western Reserve University. This project aimed to revolutionize medical education with a cadaver-less anatomy program beginning Fall 2019.
Project Context: Recruited to join Heizenrader as VP of Product, moving from a consulting role due to the opportunity with CWRU. Tasked with creating a VR educational platform for CCLCM’s innovative anatomy program.
My Role: Led product management, UX design, feature prioritization, and crafted the EducationXR brand.
Internal Team: Worked alongside Heizenrader’s CEO, CTO, and engineering leads across multiple platforms.
Contributions of Key Partners:
Zygote Medical Education designed 3D anatomical models and helped refine our authoring tools.
CCLCM’s Dr. Neil Mehta provided curriculum integration support and essential feedback and requirements from an educational perspective.
Outcome: Successfully launched the platform on time, with comprehensive technical documentation and a refined user interface.
MY ROLES
Product
Management
Research
& Strategy
UX & UI
Design
Brand
Design
User
Testing
Product
Launch
ACTIONS
We used Agile Product Management and Lean UX for the timely launch of EducationXR, conducting key UX research to define our product strategy and design process. Opting for 1-week sprints allowed rapid iteration and adaptation, supporting our expansion beyond VR to enhance accessibility and maintain interactive learning. Choosing this over traditional 2-week sprints ensured we could deliver a robust MVP quickly. Limited VR hardware availability and users’ unfamiliarity with VR influenced our push for multi-device support and intuitive designs.
Approach: Implemented Agile Product Management and Lean UX to streamline product development.
UX Research: Conducted stakeholder interviews, competitive audits, and market analyses to inform design and functionality.
Product Definition: Established a clear product vision and roadmap; developed platform architecture and prioritized features.
Design Execution: Created information architecture, user flows, wireframes, and comprehensive brand and UI design.
Agile Execution: Adopted 1-week sprint cycles for greater flexibility and faster iteration in response to real-time user feedback.
Key Decisions: Expanded hardware support beyond VR to enhance accessibility; prioritized multi-user features to maintain collaborative educational interactions.
Alternatives Considered:
Could have employed a more formal UX process or longer sprint cycles.
Potential focus solely on VR or deferring certain features until explicitly requested.
External Influences:
The 10-month deadline to align with the academic calendar.
Limited VR hardware availability and user familiarity influenced design and platform accessibility decisions.
RESULTS
The launch of EducationXR at CCLCM received positive feedback, especially for its multi-device accessibility which enhanced learning and facilitated group studies. We met our primary goals of a timely launch and swift integration of multi-user functionality. Although lacking quantitative data for comparison, qualitative feedback suggested a successful deployment. In hindsight, benchmarks against traditional programs could have offered clearer insights into our platform’s efficacy.
Positive Feedback: Faculty and students at CCLCM responded positively, appreciating the flexibility of accessing content on multiple devices.
Goal Achievement:
Launched the EducationXR platform on schedule.
Integrated multi-user group study functionality within weeks of launch.
Enhanced student engagement and educational experiences.
User Experience: Multi-platform capabilities facilitated group studies, proving advantageous over a VR-only approach.
Comparative Analysis: Lacked historical data for direct comparison with traditional methods but received positive qualitative feedback.
Potential Improvement: Future iterations could benefit from benchmarking against traditional programs to measure educational impacts more quantitatively.
LEARNINGS
This experience showed 1-week sprints effectively manage tight timelines but require careful management. This approach allowed quick adaptation to feedback and better sprint planning. We prioritized desktops over tablets for MVP, planning to involve students and faculty more in future tests. Post-launch, we switched to a design-first strategy and 2-week sprints, improving our workflow and reducing rework.
Sprint Cycles: Learned the value of 1-week sprints for high-velocity projects; found combining sprint planning and retrospectives effective.
Hardware Prioritization: Identified the need to better prioritize hardware platforms; recognized that desktop was crucial over tablet and smartphone for MVP.
User Testing: Understood the importance of incorporating faculty feedback along with student testing from early stages.
Process Adjustments:
Post-launch shifted to a proper design-test-build approach.
Transitioned to standard 2-week sprint cycles and workflow.
Future Actions: In similar future projects, will involve all key user groups in testing phases early and often to ensure comprehensive feedback.
Project Timeline
Research Phase
Stakeholder Interviews • User Personas • Competitive Audit • Market Analysis
RESEARCH PHASE
Stakeholder Interviews
Our first step in the process was to identify the key groups who would be impacted by the implementation of our completed product at CCLCM. We identified three primary groups: Anatomy Students, Anatomy Instructors, and Anatomy Department Administrators. We interviewed everyone at CCLCM that we had access to, and augmented our research with deep dives into VR education competitors and market analysis. Key issues focused on during the interview process included the following:
Clarify stakeholder expectations to align the product with their needs effectively.
Identify desired learning outcomes to shape content and measure success.
Uncover main concerns about transitioning to VR-based learning for improvements.
Assess stakeholder familiarity with VR and openness to new tech to shape user experience.
Extract crucial features and functionalities from stakeholders to guide product roadmap.
Understand hardware and infrastructure needs for successful platform implementation.
KEY INSIGHTS
The VR curriculum needed to outperform traditional methods in standardized test scores
The consensus among all stakeholders was that the VR anatomy curriculum must surpass or match the effectiveness of traditional cadaver-based methods, measured by VR students exceeding past standardized test scores.
A collaborative multi-user learning experience was a higher priority than previously estimated
Enhancing the multi-user learning experience emerged as a critical need, highlighting the importance of maintaining interactive engagements between students and teachers, as well as peer interactions. This feature would be prioritized for development immediately following the initial launch.
The VR experience should be supplemented with desktop and mobile access for broader lesson availability
Relying exclusively on VR was deemed impractical due to limited prior VR experience among users and restricted access to VR equipment. To ensure comprehensive accessibility, integrating the curriculum with desktop and mobile platforms was identified as essential to support continuous learning outside the VR lab environment.
RESEARCH PHASE
User Personas
For the EducationXR case study, the decision to create user personas based on the User Roles paradigm was a strategic choice aimed at efficiently addressing the broad and overlapping needs of our diverse user base.
“User Roles” is a persona-framework that groups users based on a shared goal, a task or a job to be done.
By focusing on the roles of a 1st-year Anatomy Student (Maya), an Anatomy Instructor (Professor Amir), and an Anatomy Department Administrator (Maria), we were able to streamline the development process, ensuring that the core functionalities of the EducationXR platform cater to the essential requirements of each key stakeholder group within the educational ecosystem.
This approach allowed us to prioritize scalability, adaptability, and the rapid iteration of features critical to enhancing the anatomy learning experience. It facilitated a clear definition of access levels, permissions, and expected interactions, making it possible to design a versatile and user-friendly VR educational platform.
Adopting the User Roles paradigm was particularly effective in the early stages of development, where understanding the fundamental needs and interactions of students, instructors, and administrators was crucial for laying a solid foundation for EducationXR's success. This method proved to be resource-efficient, enabling us to focus our efforts on delivering a high-quality, innovative learning tool that meets the practical demands of medical education today.
RESEARCH PHASE
Competitive Audit
In early 2019, my competitive audit of 20 VR educational tools highlighted the top 10's strengths and common challenges, such as accessibility and content diversity. This review also introduced 10 emerging apps, showcasing the sector's expanding range. Key findings revealed opportunities for EducationXR to address market gaps and build on existing strengths, aiming to position itself as a leader in immersive learning by enhancing user engagement and content quality.
KEY INSIGHTS
Diverse Applications with Varied Success
VR education offers diverse applications across subjects like anatomy and history, showcasing its potential. Yet, its success and acceptance varies across disciplines and user groups, reflecting a very mixed landscape.
Challenges in Replicating Hands-On Experiences
Both users and competitors acknowledge VR's struggle to match the depth of hands-on experiences, especially in tactile fields like anatomy. This reveals a market gap for VR that can effectively replicate or enhance real-world learning.
Significant Integration and Adoption Hurdles
The competitive analysis highlights challenges in VR adoption and integration by educators, stressing the need for intuitive, user-friendly VR platforms with strong support to facilitate effective curriculum integration.
Numerous Technological and Accessibility Barriers
Growing interest in VR education faces challenges like hardware needs, maintenance, and user learning curves. Cost and IT infrastructure requirements hinder its widespread adoption, especially in under-resourced schools.
Widely-held Aspirations for Scalability and Customization
The analysis reveals demand for scalable, customizable VR platforms to meet diverse educational needs, presenting an opportunity for differentiation through adaptable, personalized learning experiences.
RESEARCH PHASE
Market Analysis
My market analysis for EducationXR dug into an array of sources to capture a comprehensive view of the VR education sector as of January 2019. This ensured our analysis was grounded in diverse, expert perspectives, positioning EducationXR at the forefront of educational innovation. This included the following:
Market research from Gartner and Harris Interactive
White papers and case studies from Google and Oculus
Articles from EdTech Magazine, VRScout, The Verge, and TechCrunch
My aim was to identify the unique opportunities and challenges within the VR educational sector, offering a clear understanding of how EducationXR can carve out a niche by addressing unmet needs and capitalizing on emerging trends.
Definition Phase
Product Vision & Goal • Platform Architecture • Feature Prioritization • Product Roadmap
DEFINITION PHASE
Product Vision
“EducationXR will transform the future of education through immersive VR experiences, aiming to set a new standard for interactive learning in academia and industry by 2020. EducationXR will revolutionize learning and training across various fields with a versatile VR platform, bridging the gap between traditional learning methods and future needs in both academic and commercial environments through immersive, scalable, and user-centric educational experiences.”
SMART GOAL
“By September 2019, launch EducationXR, a VR-based learning platform for Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, to provide an enhanced educational experience that outperforms traditional methods, as measured by student comprehension rates.”
SPECIFIC
Develop an immersive and interactive VR-based learning platform, EducationXR, to surpass traditional textbook and cadaver-based anatomy education methods.
MEASURABLE
Evaluate the effectiveness of EducationXR by comparing student averages on relevant tests taken during the first semester of use with historical averages from previous terms.
ACHIEVABLE
Assemble a dedicated product team by February 2019 to lead development of individual product areas, ensuring the platform is ready for deployment.
RELEVANT
Target the implementation of EducationXR for CCLCM’s Year 1 and Year 2 anatomy students, aligning with the curriculum's specific needs and enhancing the overall learning experience.
TIME-BOUND
Launch EducationXR at the beginning of the Fall 2019 semester, ensuring all content, user management, and support structures are fully operational by September 2019.
DEFINITION PHASE
Platform Architecture
The development of EducationXR demanded an architecture that catered to the current needs of CCLCM while remaining flexible for future scalability across diverse educational sectors. Our approach was to design a multi-tiered architecture that would support a variety of educational and training modules for different user groups.
Content Authoring Layer: This is the creative hub where educators build lessons through our customized Unity plugins, streamlining content production and ensuring data is accurately aligned for the user experience. The layer allows for direct publishing to our Curriculum Management Layer.
Curriculum Management Layer: Serving as the data core, this repository layer is the backbone of content storage and management. It is fortified with a firewall and seamlessly interfaces with a sophisticated Services Layer, which comprises:
Content Service: Facilitates lesson content access and management
Analytics Service: Captures detailed usage and engagement statistics
Identity Service: Manages user authentication and database access
Tethering Service: Orchestrates synchronized multi-user sessions, enabling interactive group studies
Admin Interface: A web-based control panel through which administrators manage course content, user profiles, and analytics.
Education Portal Layer: This layer is the gateway for students and instructors to engage with the curriculum through an intuitive interface across a spectrum of device ecosystems, including SteamVR, Windows Mixed Reality, desktop, tablet, and mobile platforms.
App Store Distribution: Committed to a streamlined user experience, content is delivered through native apps available on device-specific app stores, simplifying update rollouts and ensuring a familiar, secure experience for all users.
Our architectural design provides the backbone for a scalable, secure, and accessible VR education platform, ensuring EducationXR meets and adapts to the evolving needs of learners and educators.
DEFINITION PHASE
Feature Prioritization
As the Product Manager, my collaboration with the Head of Engineering (CTO), our engineering team, and the Head of Biz Dev (CEO), was pivotal in defining the feature set required to achieve the product vision of EducationXR. Following the architecture outline, we embarked on a detailed feature identification process, categorizing the features into three core areas: Admin Portal, In-Lesson, and Lesson Launcher functionalities.
We used the MoSCoW method for feature prioritization, sorting them into 'Must Have', 'Should Have', 'Could Have', and 'Won't Have' categories. This structured approach was critical for mapping features into our development timeline and key product milestones.
DEFINITION PHASE
Product Roadmap
Leveraging the MoSCoW method for feature prioritization was instrumental in aligning our expansive list of features with a production timeline that adhered to our aggressive development schedule. This technique facilitated the clear delineation of essential features, allowing us to sequence the build in a manner that ensured the most critical components, classified as 'Must Haves,' were developed first to fulfill the core objectives of EducationXR. Managing the product roadmap through Agile Product Management methodology, we adopted 1-week Sprints that provided the flexibility and responsiveness needed to adapt to evolving project demands. Daily stand-up meetings were crucial touchpoints that kept the cross-functional team aligned on progress, impediments, and immediate next steps, ensuring that our pathway from MVP to final product was navigated with precision and efficiency, maintaining momentum towards our targeted milestones.
Design Phase
User Flows • Wireframes • Brand Design • UI Design
DESIGN PHASE
User Flows
Crafting user flows is a critical step in the design process, as it outlines the path a user follows through an application to complete specific tasks. This process is vital because it focuses on the user experience, ensuring that the journey through the software is intuitive, efficient, and aligns with user expectations. For EducationXR, developing user flows was essential to create an immersive educational environment that is both accessible and engaging. It ensured that students and educators could navigate seamlessly between lessons, access content, and utilize collaborative tools without friction. By meticulously mapping out these flows, we addressed potential pain points and streamlined interactions, laying the foundation for a platform that enhances learning through technology and interaction design, reinforcing EducationXR's commitment to delivering an innovative and user-centric educational experience.
DESIGN PHASE
Brand Design
For EducationXR, I crafted a brand identity that reflects the platform's fresh, engaging approach to virtual reality in education. The visuals are anchored in a modern palette, appropriate for the interactive VR experience. Our style guide is intuitive, ensuring that every touchpoint – from the interface to marketing materials – resonates with clarity, impact, and a consistent visual language.
DESIGN PHASE
UI Design
Virtual Reality UI
Desktop UI
Mobile UI
Admin UI
LAUNCH PHASE
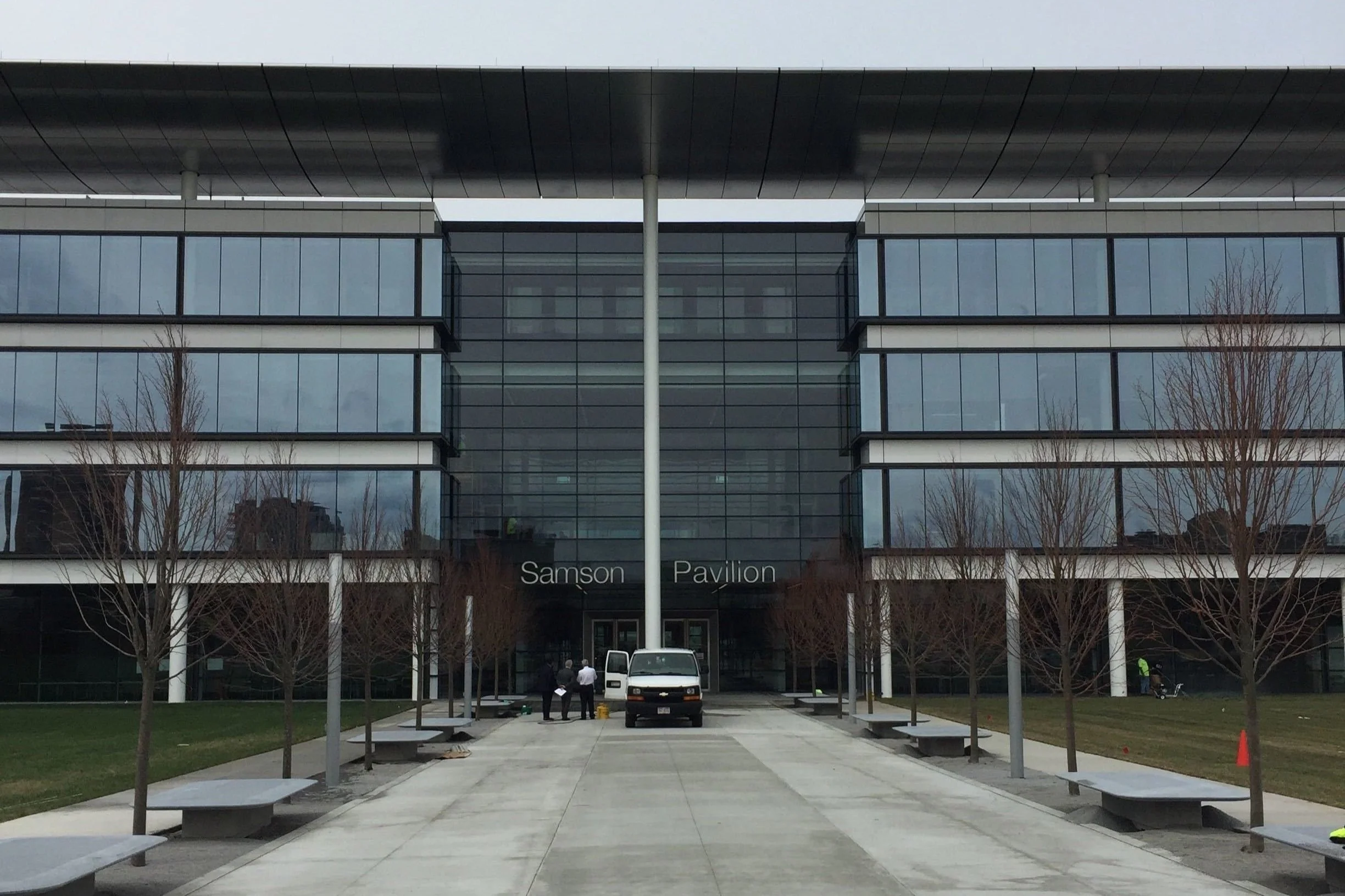
Go-to-Market Deployment at CCLCM Campus
EducationXR was first deployed in the Samson Pavilion at the Cleveland Clinic Learner College of Medicine. A large classroom was set up as the Anatomy Lab with multiple VR stations permanently installed. This is where 1st and 2nd year students had Anatomy Lab would meet for classes based on their schedules.
LAUNCH PHASE
User Guide
EVALUATION PHASE
User Feedback: Six Key Learnings
As we reflect on the launch of EducationXR at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, certain key insights stand out, shaping the future trajectory of our platform. These insights, drawn from user feedback, not only validate our initial research but also chart the course for continuous improvement. Here are the pivotal learnings from our successful deployment.
Cross-Platform Capabilities Key to Student Success
Expanding beyond VR to include laptop and mobile access proved invaluable. Students praised the flexibility of reviewing content across devices, significantly enhancing study practices and academic performance, distinguishing EducationXR as a versatile tool.
Administrators Desire In-Depth Engagement Analytics
Beyond the MVP, administrators sought detailed analytics for deeper engagement insights. They expressed the need to track user interactions, device preferences, and time spent, aiming to tailor and improve the educational delivery.
Multi-User Feature Tops User Wish List Post-Launch
Upon launch, EducationXR met CCLCM's criteria, with user feedback underscoring the value of collaborative learning. This initial insight informed our post-launch strategy, prioritizing multi-user functionality and essential bug fixes as our engineering team's primary focus.
Guided Lessons Expand EducationXR’s Institutional Appeal
The demand for guided, instructor-led virtual experiences was evident, resonating with medical and industrial sectors. Incorporating 'virtual instructor' functionality aligns with our expansion goals, opening new markets for EducationXR.
Streamlined VR Navigation Enhances User Experience
The default VR teleportation controls, while standard, proved disorienting for VR novices. The need for intuitive, simplified navigation became apparent, guiding our updates to enhance user comfort and lesson absorption.
Demand Surges for Multilingual EducationXR Content
Responding to CCLCM's diverse and multilingual student body, the call for native language support was clear. Embracing language localization emerged as a strategic move, paving the way for global reach and inclusivity in education.